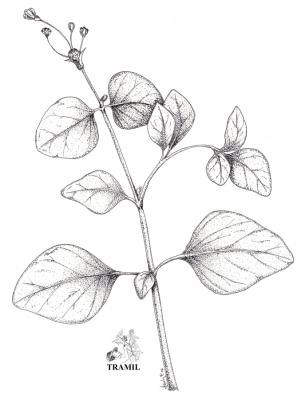
Boerhavia diffusa
Noms vernaculaires
(dans les territoires avec usage significatif TRAMIL)
Martinique:
- patagon
Distribution géographique
Régions tropicales et subtropicale.
Description botanique
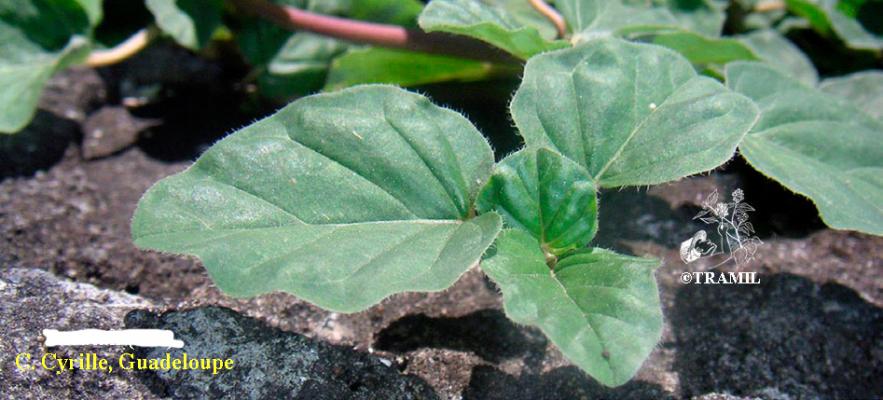
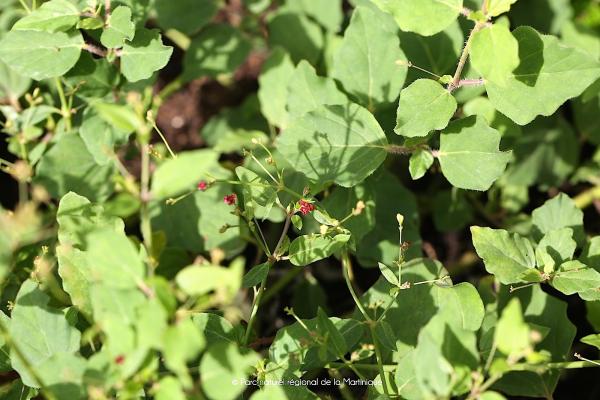
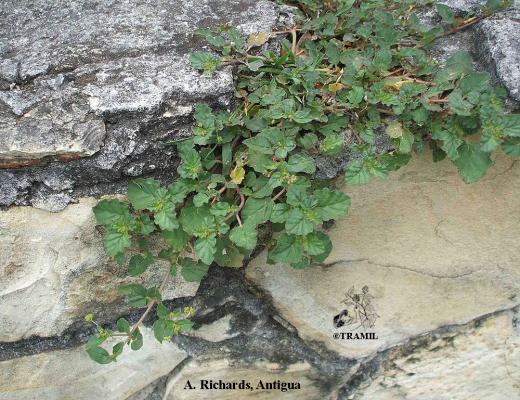
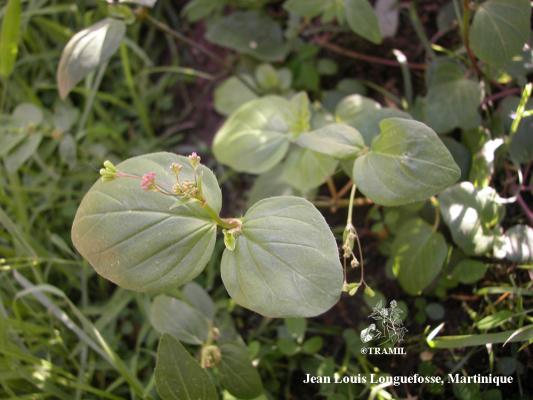
Herbacée vivace jusqu’à 1 m. Feuilles suborbiculaires, ovées ou ovales, de 2-5 cm, apex obtus à arrondi, parfois aiguë, arrondies à la base, plus pâles sur le dessous. Fascicules de fleurs disposées en panicules longs, petites fleurs, calice de 1,5 à 2 mm et limbe de 0,8 à 0,9 mm en capitules formant des cymes, périanthe rouge-pourpre. Fruit obovoïde, de 2,5 à 3 mm, à 5 angles.
Voucher(s)
Longuefosse & Nossin, 5, HAVPM
Pharmacopée
Ed.3References
1 LONGUEFOSSE JL, NOSSIN E, 1990-95
Enquête TRAMIL. Association pour la valorisation des plantes médicinales de la Caraïbe AVPMC, Fort de France, Martinique.
2 Beltran C, Jimenez S, GOmez A, BeltrAn J, GarcIa G, GOmez H, 2010
screening fitoquimico de hoja de Boerhaavia diffusa (infusión, deccoción y extracto etanólico (maceración). Trabajo TRAMIL. Grupo de Investigación en Química de Medicamentos, Universidad de Cartagena, Colombia.
3 AGARWAL RR, DUTT SS, 1934
Chemical examination of punar-nava or Boerhavia diffusa Linn. Proc Acad Sci 4:73-76.
4 MATHAMS RH, SUTHERLAND AK, 1952
The oxalate content of some Queensland pasture plants. Queensland J Agric Sci 9:317-334.
5 AHMAD K, HOSSAIN A, 1968
Isolation, structure, synthesis and biological action of hypoxanthine-9-L-arabinofuranoside. Pak J Biol Agr Sci 11(2):41-44.
6 AGARWAL RR, DUTT SS, 1935
Chemical examination of punarnava or Boerhavia diffusa Linn. II Isolation of an alkaloid punarnavine. Proc Acad Sci United Provinces Agra Audh India 5:240-242.
7 BASU NK, LAL SB, SHARMA SN, 1947
Investigations on Indian medicinal plants. Q J Pharm Pharmacol 20(1):38-42.
8 SRIVASTAVA DN, SINGH RH, UDUPA KN, 1972
Studies on the Indian indigenous drug, punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa Linn.). Part V. Isolation and identification of a steroid. J Res Indian Med 7(3):34-36.
9 ROIG J, 1988. Plantas Medicinales, Aromáticas y Venenosas de Cuba. 2a ed. La Habana, Cuba: Editorial Científico-Técnica.
10 FERRERES F, SOUSA C, JUSTIN M, VALENTÃO P, ANDRADE PB, LLORACH R, RODRIGUES A, SEABRA RM, LEITÃO A, 2005
Characterisation of the phenolic profile of Boerhaavia diffusa L. by HPLC-PAD-MS/MS as a tool for quality control. Phytochem Anal 16(6):451-458.
11 PEREIRA DM, FARIA J, GASPAR L, VALENTÃO P, DE PINHO PG, ANDRADE PB, 2009
Boerhaavia diffusa: metabolite profiling of a medicinal plant from Nyctaginaceae. Food Chem Toxicol 47(8):2142-2149.
12 CACERES A, GONZALEZ S, GIRON L, 1998
Demostración de la actividad antimicrobiana de plantas TRAMIL en base a los usos populares en la cuenca del Caribe. Laboratorio de productos fitofarmacéuticos Farmaya y Facultad de Ciencias Químicas y Farmacia, Universidad de San Carlos, Guatemala, Guatemala.
13 SOUZA BRITO AR, HIRUMA-LIMA CA, 1996
Toxicidade aguda e atividade analgésica de estratos brutos de plantas do Caribe. Informe TRAMIL. Dep. de Fisiología y Biofísica, Universidad de Campinas, Campinas, Brasil.
14 HIRUMA-LIMA CA, GRACIOSO JS, BIGHETTI EJB, GERMOSEN-ROBINEAU L, SOUZA BRITO AR, 2000
The juice of fresh leaves of Boerhavia diffusa L. (Nyctaginaceae) markedly reduces pain in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 71(1/2):267-274.
15 AYNEHCHI Y, SALEHI SORMAGHI M, SHIRUDI M, 1982
Screening of Iranian plants for antimicrobial activity. Acta Pharm 19(4):303-308.
16 ORISAKWE OE, AFONNE OJ, CHUDE MA, OBI E, DIOKA CE, 2003
Sub-chronic toxicity studies of the aqueous extract of Boerhavia diffusa leaves. J of Health Science 49(6)444-447.
17 CHANDAN BK, SHARMA AK, ANAND KK, 1991
Boerhavia diffusa: a study of its hepatoprotective activity. J Ethnopharmacol 31(3):299-307.