Noms vernaculaires
(dans les territoires avec usage significatif TRAMIL)
Haïti:
- koray
- koway
Distribution géographique
Amérique tropicale.
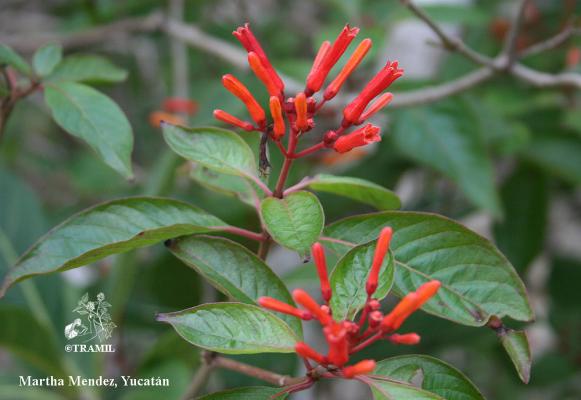
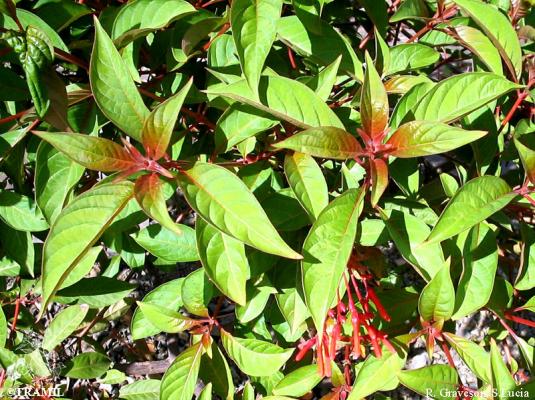
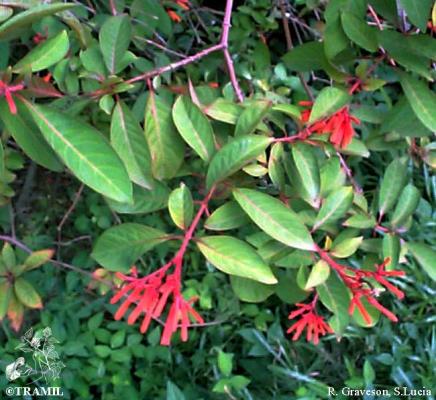
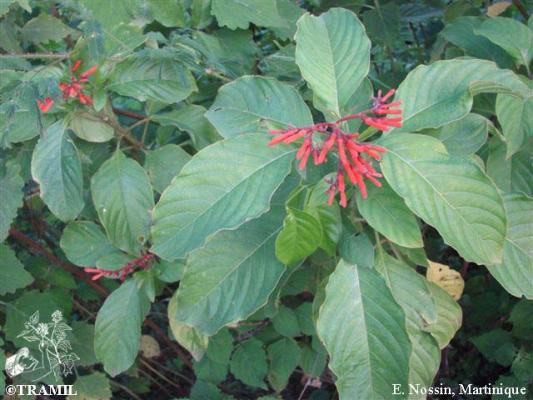
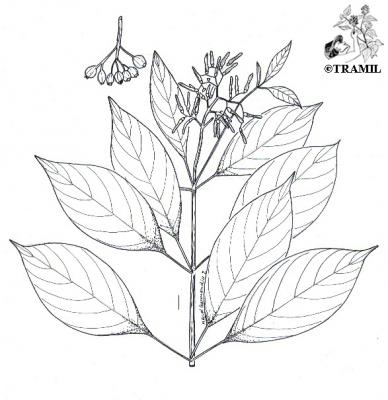
Description botanique
Arbuste ou petit arbre, pouvant atteindre 4 m. Feuilles à trois lobes, elliptiques à elliptico-oblancéolées, de 5 à 21 cm, courtement acuminées. Inflorescence de 3 à 15 cm de long; corolle tubulaire de 1,5 à 2 cm, orangée ou rougeâtre, pubérulente. Fruit sub-ovoïde ou ellipsoïdal, de 6 à 10 mm, rougeâtre quand il est jeune puis noir à maturité.
Voucher(s)
Rouzier, 161, SOE
Jiménez, 32, JBSD
Pharmacopée
Ed.3References
1 WENIGER B, ROUZIER M, 1986
Enquête TRAMIL. Service Oecuménique d'Entraide SOE, Port au Prince, Haïti.
2 MENDEZ M, MEDINA ML, DURAN R, 1996
Encuesta TRAMIL en Quintana Roo. Unidad de recursos naturales, Centro de Investigación Científica de Yucatán CICY, Mérida, México.
3 ESPOSITO-AVELLA M, GUPTA M, 1986
Evaluación fitoquímica y farmacológica de Hamelia patens y Terminalia catappa. Centro de Investigaciones Farmacognósticas de la Flora Panameña CIFLORPAN, Facultad de Farmacia, Universidad de Panamá, Panamá, Panamá.
4 ESPOSITO-AVELLA M, BROWN P, TEJEIRA I, BUITRAGO R, BARRIOS L, SANCHEZ C, GUPTA MP, CEDENO J, 1985
Pharmacological screening of Panamanian medicinal plants. Part I. Int J Crude Drug Res 23(1):17-25.
5 REYES-CHILPA R, RIVERA J, OROPEZA M, MENDOZA P, AMEKRAZ B, JANKOWSKI C, CAMPOS M, 2004
Methanol extracts of Hamelia patens containing oxindole alkaloids relax KCl-induced contraction in rat myometrium. Biol Pharm Bull 27(10):1617-1620.
6 RIPPERGER H, 1977
Isolation of isopteropodine from Hamelia patens. Pharmazie 32(H7):415-416.
7 BORGES DEL CASTILLO J, MANRESA MT, RODRIGUEZ F, 1981
Oxindole alkaloids from Hamelia patens Jacq. Proc 1st Int. Conf. Chem. Biotechnol. Biol. Acta Nat. Prod., Sofia, Bulgaria. Bulgarian Acad Sci Sofia 3(1):70-73.
8 CHAUDHURI PK, THAKUR RS, 1991
Hamelia patens, a new source of ephedrine. Planta Med 57(2):199.
9 ADAMS AA, LEE EF, MABRY TJ, 1989
HPLC study of oxindole alkaloids from Hamelia patens. Rev Latinoamer Quim 20(2):71-72.
10 AQUINO R, CIAVATTA L, DE SIMONE F, PIZZA C, 1990
A flavanone glycoside from Hamelia patens. Phytochemistry 29(7):2358-2360.
11 GUPTA M, ESPOSITO-AVELLA M, 1988
Evaluación química y farmacológica de algunas plantas medicinales de TRAMIL. Centro de Investigaciones Farmacognósticas de la Flora Panameña CIFLORPAN, Facultad de Farmacia, Universidad de Panamá, Panamá, Panamá.
12 MISAS C, HERNANDEZ N, ABRAHAM A, 1979
Contribution to the biological evaluation of Cuban plants. I. Rev Cub Med Trop 31(1):5-12.
13 CARBALLO A, 1995
Plantas medicinales del Escambray cubano. Apuntes científicos. Laboratorio provincial de producción de medicamentos, Sancti Spiritus, Cuba.
14 CACERES A, GIRON L, ALVARADO S, TORRES M, 1987
Screening of antimicrobial activity of plants popularly used in Guatemala for the treatment of dermatomucosal diseases. J Ethnopharmacol 20(3):223-237.
15 NEGWER M, 1987
Organic chemical drugs and their synonyms (an international survey). 6th ed. Berlin, Germany: Akademie Verlag.
16 DUKE J, 1992
Handbook of biologically active phytochemicals and their bioactivities. Boca Raton, USA: CRC Press.
17 LAMAISON J, PETITJEAN-FREYTET C, CARNAT A, 1990
Rosmarinic acid, total hydroxycinnamic derivative contents and antioxidant activity of medicinal Apiaceae, Boraginaceae & Lamiceae. Ann Pharm Fr 48(2):103-108.
18 LOPEZ M, MOREJON Z, BOUCOURT E, GARCIA AI, 2011
Ausencia de irritabilidad dérmica primaria de decocción de hoja seca de Hamelia patens (ponasí). Informe TRAMIL. Laboratorio Central de Farmacología, Facultad de Ciencias Médicas “Dr. Salvador Allende”, La Habana, Cuba.
19 LOPEZ M, MOREJON Z, BOUCOURT E, GARCIA AI, 2011
Ausencia de irritabilidad dérmica primaria de decocción de flor de Hamelia patens (ponasí). Informe TRAMIL. Laboratorio Central de Farmacología, Facultad de Ciencias Médicas “Dr. Salvador Allende”, La Habana, Cuba.