Acalypha alopecuroidea
Noms vernaculaires
(dans les territoires avec usage significatif TRAMIL)
République dominicaine:
- ajito con pelo
Haïti:
- dégonflé
Distribution géographique
Originaire de l'Amérique tropicale.
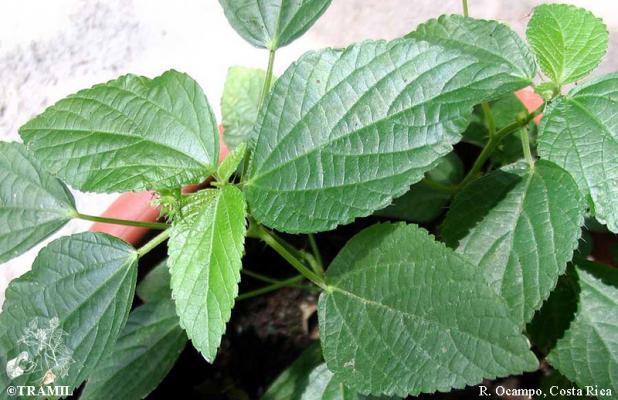
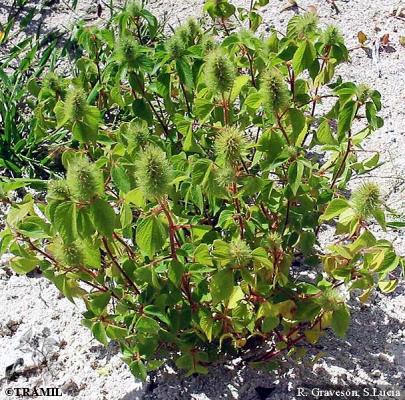
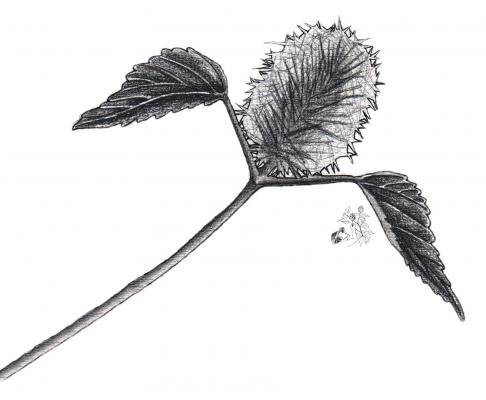
Description botanique
Herbacée droite, annuelle, pouvant atteindre 50 cm. Feuilles de forme triangulaire à arrondie-ovale, de 3 à 7 cm, acuminées ou cuspido-acuminées, denticulées. Épis terminaux et axillaires, pouvant atteindre 5 cm; bractées de fleurs portant pistil de 7 à 9 mm, avec de longs poils. Capsule de 2 mm de long.
Voucher(s)
Rouzier, 59&61, SOE
Jiménez, 215, JBSD
Pharmacopée
Ed.3References
1 WENIGER B, ROUZIER M, 1986
Enquête TRAMIL. Service Oecuménique d'Entraide SOE, Port au Prince, Haïti.
2 GERMOSÉN-ROBINEAU L, GERÓNIMO M, AMPARO C, 1984
Encuesta TRAMIL. enda-caribe, Santo Domingo, Rep. Dominicana.
3 WENIGER B, SAVARY H, DAGUIHL R, 1984
Tri phytochimique de plantes de la liste TRAMIL. Rapport TRAMIL. Faculté de Médecine, Université de Haïti, Port au Prince, Haïti.
4 HEGNAUER R, 1973
Chemotaxonomie der Pflanzen. Eine Übersicht über die Verbreitung und die systematische Bedeutung der Pflanzenstoffe. 6, Dicotyledoneae: Rafflesiaceae — Zygophyllaceae. Basel und Stuttgart, Deutschland: Birkhäuser Verlag.
5 HOSTETTMANN K, LEA PJ, 1987
Biologically active natural products. Oxford, England: Oxford Science Publications.
6 DUKE JA, 1992
Handbook of phytochemical constituents of GRAS herbs and other economic plants. Boca Raton, USA: CRC Press.
7 LE GRAND A, WONDERGEM PA, 1986
Activités antimicrobiennes et études bibliographiques de la toxicologie de dix plantes médicinales de la Caraïbe. Rapport TRAMIL. Dép. de Pharmacognosie, Universités de Groningen & Leyden, Groningen & Leyden, Hollande.
8 DEL ROSARIO PEREZ R, WENIGER B, 1988
Activité d’Acalypha alopecuroidea sur intestin isolé. Travail TRAMIL. Université de Strasbourg, Strasbourg, France.
9 MORÓN F, BETANCOURT J, PINEDO Z, BOUCOURT E, 2000
Efecto de hoja fresca de Acalypha alopecuroidea Jacq. en el tránsito intestinal de ratones in vivo. Informe TRAMIL. Laboratorio Central de Farmacología, Facultad de Ciencias Médicas “Dr. Salvador Allende”, La Habana, Cuba.
10 MARTÍNEZ MJ, BETANCOURT J, LÓPEZ M, MOREJÓN Z, BARCELO H, LAINEZ A, MONTES ME, REGO R, BOUCOURT E, MORÓN F, 2000
Toxicidad aguda de hoja fresca de Acalypha alopecuroidea Jacq. en el modelo de clases tóxicas agudas. Informe TRAMIL. Laboratorio Central de Farmacología, Facultad de Ciencias Médicas “Dr. Salvador Allende”, La Habana, Cuba.
11 SOUZA BRITO A, 1995
Toxicidad aguda de Acalypha alopecuroidea. Informe TRAMIL. Dep. de Fisiología y Biofísica, Universidad de Campinas, Campinas, Brasil.
12 POULTON J, KEELER R, TU T, 1983
Handbook of natural toxins 1. New York, USA: Marcel Dekker, p117.
13 NAHRSTEDT A, 1987
Recent developments in chemistry, distribution and biology of the cyanogenic glycosides. In: Hostettmann K, Lea PJ. Biologically active natural products. Oxford, USA: Oxford Science Publications. p167-184,213-234.
14 ARGEHEORE EM, AGUNBIADE OO, 1991
The toxic effects of Cassava (Manihot esculenta Grants) diets on humans: a review. Hum Toxicol 33(3):273-275.