Cardiospermum halicacabum
Vernacular names
(In territories with significant traditional TRAMIL use)
Martinique:
- boné karé
Geographical distribution
Widely distributed in the tropics and subtropics of the New and Old World.
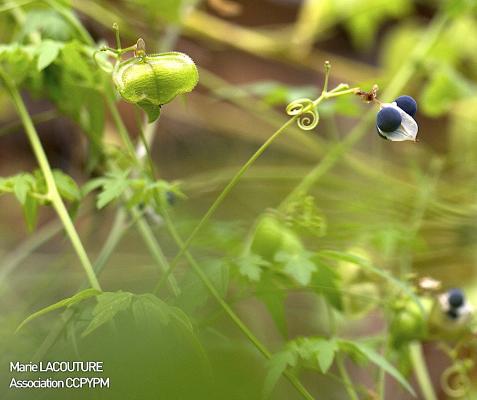
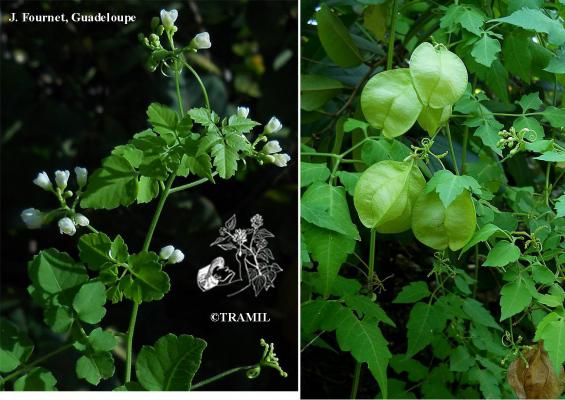
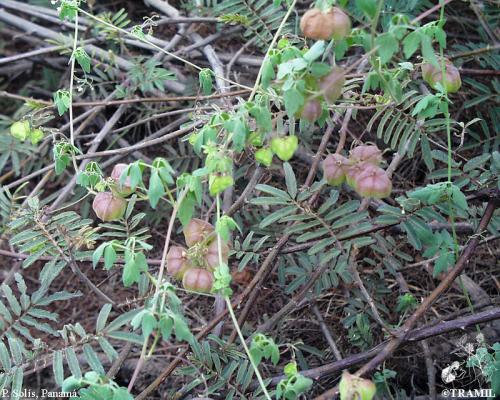
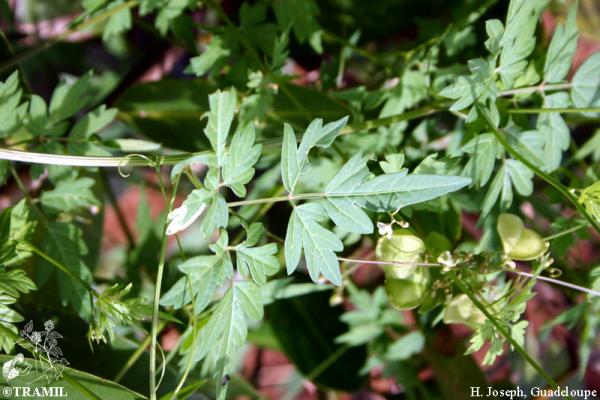
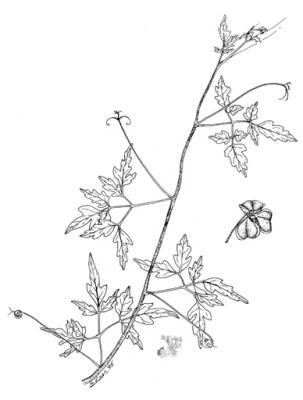
Botanical description
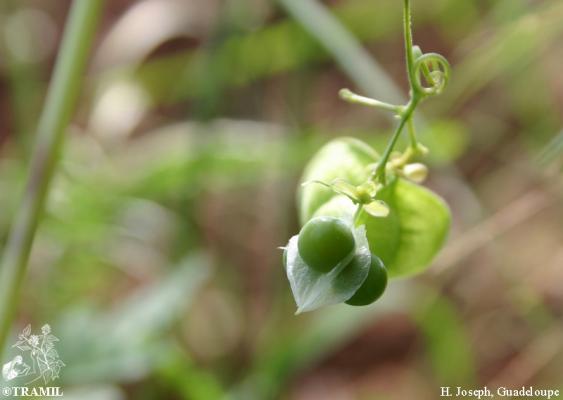
Herbaceous climber with a 5 to 6 m long ribbed stem. Leaves biternate, folioles ovate or lanceolate, acute or acuminate, serrated or lobed. Umbelliform inflorescence with long peduncles and white flowers of 4 to 5 mm. Subglobose capsule from 3 to 4 cm; black seeds from 4 to 5 mm.
Voucher(s)
Nossin,6,HAVPM
Pharmacopoeia
Ed.3References
1 LONGUEFOSSE JL, NOSSIN E, 1990-95
Enquête TRAMIL. Association pour la valorisation des plantes médicinales de la Caraïbe AVPMC, Fort de France, Martinique.
2 SOLIS P, GUPTA M, CORREA M, 1996
Estudio fitoquímico de algunas plantas TRAMIL. Informe TRAMIL. Centro de Investigaciones Farmacognósticas de la Flora Panameña CIFLORPAN, Facultad de Farmacia, Universidad de Panamá, Panamá, Panamá.
3 KUMARESAN A, 1981
Phytochemical investigation of the leaves of the plant Cardiospermum halicacabum Linn. Indian J Pharm Sci 43.
4 PATIL AG, JOSHI KA, PATIL DA, PHATAK AV, NARESH C, 2010
Pharmacognostic and physico-chemical studies on the leaves of Cardiospermum halicacabum L. Phamacognosy J 8(2):44-49.
5 MECKLINGER S, MESSEMER C, NIEDERLE S, 1995
Eksembehandlung mit Cardiospermum halicacabum. Cardiospermum-Salbe und Salbengrundlage im Halbseitenvergleich. Eine kontrollierte Studie. Zeitschrift für Phytotherapie 16(5):263-266.
6 KHANNA MSY, JAVED K, KHAN MH, 1990
Chemical examination of Cardiospermum halicacabum Linn. Indian Drugs 24(4):257-258.
7 SHABANA MM, GENENAH AA, EL ZALABANI SM, ABOU EL-ELA RG, YOUSIF MF, 1990
Phytochemical investigation and insecticidal activity of Cardiospermum halicacabum L. Cultivated in Egypt. Bull Fac Pharm Cairo Univ 28(2):79-83.
8 HERRERA J, 1996
Validación farmacológica de plantas medicinales usadas en medicina tradicional popular en la cuenca del Caribe. Informe TRAMIL. Dep. de Farmacología, Facultad de Salud, Universidad del Valle, Cali, Colombia.
9 MURUGESAN S, VIJI M, 2010
Phytochemical analysis and antibacterial activity of medicinal plant Cardiospermum halicacabum Linn. J Phytology 2(1):68-77.
10 CHANDRA T, SADIQUE J, 1984
Antiinflammatory effect of the medicinal plant Cardiospermum halicacabum Linn. In vitro study. Arogya 101:57-60.
11 ASHA VY, PUSHPANGADAN P, 1999
Antipyretic activity of Cardiospermum halicacabum. Indian J Exp Biol 37(4):411-414.
12 MENG Z, SAKAI Y, OSE Y, SATO T, NAGASE H, KITO H, SATO M, MIZUNO M, ONO K, NAKANE H, 1990
Antimutagenic activity by the medicinal plants in traditional Chinese medicines. Shoyakugaku Zasshi 44(3):225-229.
13 HORMANN H, KORTING H, 1994
Evidence for the efficacy and safety of topical herbal drugs in dermatology: Part I: anti-inflammatory agents. Phytomedicine 1(2):161-171.